Theories of Interest
Some Thoughts & Notes have evolved from readings in these Directions
Deconstruction : Deconstruction’s philosophical basis is a questioning of established Western authoritarian concepts. In literary (or other) criticism, analysis of texts is based on a profound skepticism concerning the stability of meaning in language. The deconstructive critic does not seek a central interpretation, but lets the mind play with presuppositions and intertextualities.
Emergence Theories : Theories of the development of some phenomenon (for example life consciousness) where something emerges out of the background from which it could not have been predicted and in terms of which it cannot be fully explained.
Reductionism : The reducing of certain kinds of entities, or of theories, or even whole sciences, to other, more basic ones. Entities that are reduced may be replaced (Water is really H2O).
Big Bang Theory : A cosmological theory that attempts to explain the origin of matter and radiation in the universe in terms of a cataclysmic explosion supposed to have occurred 10-20 billion years ago. Elementary particles and anti-particles were created within a fraction of a second after the Big Bang, followed by photons of radiation. In the following minutes Deuterium and Helium nuclei formed, followed by neutral Hydrogen atoms where the temperature dropped sufficiently.
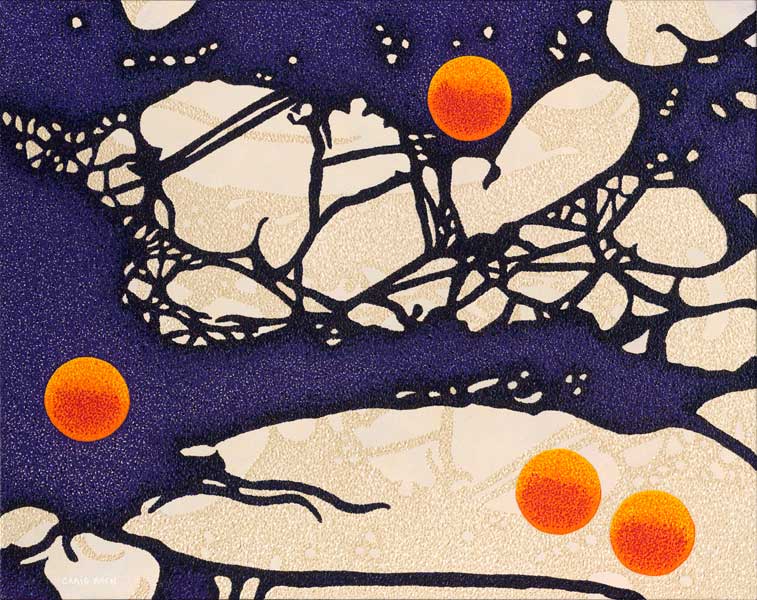
Pointillism : In art, a technique closely related to Divisionism, first systematically applied by French painter Georges Seurat (1859-91) in his La Grand Jatte (1886). Following the theories of Charles Blanc and Ogden N. Rood, Seurat developed a technique of applying pigment of complementary color in small dots which are additively mixed by the eye at a certain distance. The method thereby achieved more luminous color and ensured a more controlled handling of tone.
Divisionism : In art, a name first used by artist Paul Signac (1863-1935) for a method of painting with pure color which later developed into scientific Pointillism. Signac proposed that to achieve the brightest and purest color, all those of the spectrum should be used, applied in small daubs or dots of unmixed pigment which vary according to the size of the painting. At a distance, these fuse in the spectator’s eye.
Abstract Art : Art that is synonymous with ‘abstraction,’ this term has been applied since the first decades of the 20th century to describe non-representational painting; a style which persists today. Although elaborated upon and refined in its precise manifestations, abstract art essentially compromises non-figurative art, as first exemplified by the color abstracts of Russian painter Wassily Kandinsky (1866-1944) around 1911. It then developed into Cubism and later, on an international scale, Abstract Expressionism.
Dark Matter Theory : In Astronomy, Dark Matter is non-baryonic matter (overarching name for subatomic particles such as protons, neutrons, and electrons) which does not interact with radiation and is therefore ‘dark’ for all astronomical purposes. It is thought to comprise 90 percent of the matter of the universe and can only be detected by its gravitational effects.
Metaphor : From the Greek words meta pherein, meaning carry over, transfer. In Western tradition theory of metaphor originates with the Greek philosopher Aristotle (384-322 BC). Traditionally very important in modern theories of language. Reference to one object in terms of another, so that features of the second are transferred to the primary referent.
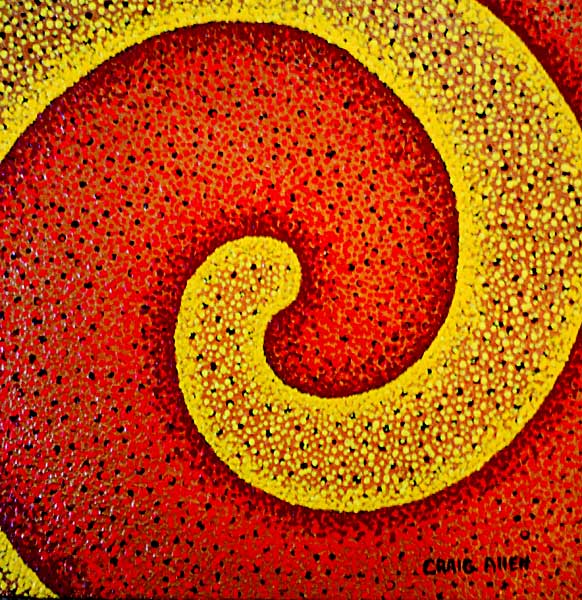
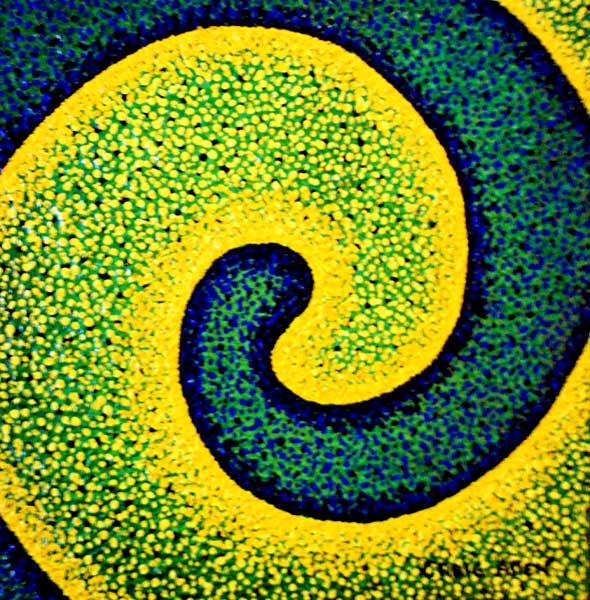
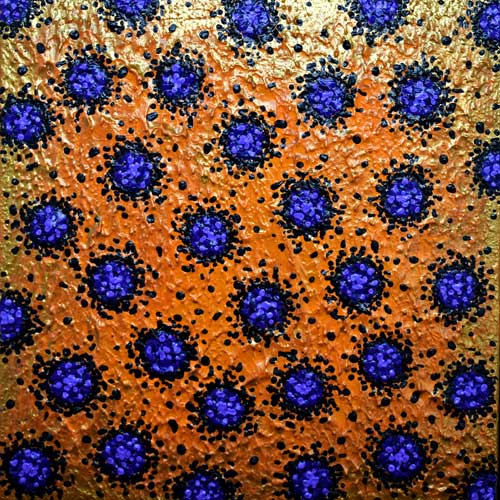
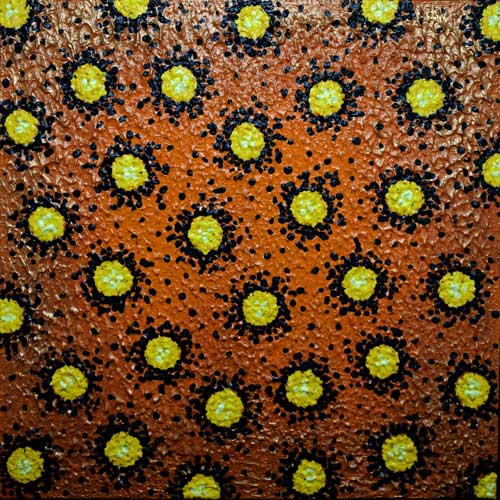


















































































































Facebook: Craig Allen Lawver Art